Applications and Types of Directional Couplers in Communication Networks
Directional couplers are essential components in communication networks, widely used for their ability to split, combine, or sample signals while maintaining directionality. Below, I’ll outline their applications and types, providing a concise yet comprehensive overview based on their role in modern systems.
Applications of Directional Couplers in Communication Networks

Signal Monitoring and Measurement
Directional couplers are used to sample a portion of the signal in a transmission line without interrupting the main flow. This is critical in network diagnostics, such as measuring power levels, signal integrity, or detecting faults in RF and microwave systems like cellular base stations or satellite communications.Power Division and Distribution
They split an input signal into multiple outputs with a defined coupling ratio (e.g., 3 dB, 10 dB). This is vital in feeding multiple antennas in phased array systems or distributing signals in distributed antenna systems (DAS) for wireless networks.Mixing and Combining Signals
In reverse, they can combine signals from different sources, such as in multiplexing applications or when aggregating signals in fiber-optic networks or hybrid RF systems.Impedance Matching and Tuning
By sampling reflected signals, directional couplers help adjust impedance in amplifiers or transmitters, optimizing performance in high-frequency communication systems like radar or 5G networks.Beamforming and Antenna Systems
In advanced networks (e.g., 5G or satellite), they enable precise control of signal phases and amplitudes, supporting beamforming techniques for directional signal transmission.Test and Calibration
Labs and field engineers use them in spectrum analyzers or vector network analyzers (VNAs) to calibrate equipment or test system performance under real-world conditions.
Types of Directional Couplers
Branch-Line Couplers
Structure: Composed of four ports with two parallel transmission lines connected by branch lines.
Characteristics: Typically a 3 dB (equal split) coupler with 90° phase difference between outputs.
Use: Common in microwave integrated circuits (MICs) and phased array antennas.
Coupled-Line Couplers
Structure: Two parallel transmission lines placed close together, allowing electromagnetic coupling.
Characteristics: Adjustable coupling factor (e.g., 10 dB, 20 dB); operates over a wide bandwidth.
Use: RF signal sampling in cellular networks or broadband systems.
Hybrid Couplers
Structure: Four-port devices, often 3 dB, with 90° or 180° phase shifts (e.g., quadrature or rat-race couplers).
Characteristics: Equal power division with high isolation between ports.
Use: Balanced amplifiers, mixers, or antenna feed networks in wireless communications.
Stripline/Microstrip Couplers
Structure: Built using planar transmission lines on a dielectric substrate.
Characteristics: Compact, cost-effective, and easy to integrate into PCBs.
Use: Widely used in compact RF modules for Wi-Fi, IoT, or satellite transceivers.
Waveguide Couplers
Structure: Hollow metallic waveguides with slots or apertures for coupling.
Characteristics: High power handling and low loss, suited for microwave frequencies.
Use: Radar systems, satellite uplinks, and high-power microwave networks.
Optical Directional Couplers
Structure: Fiber-optic or planar waveguide-based, splitting light signals.
Characteristics: Low insertion loss, used in wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM).
Use: Core component in fiber-optic communication networks like FTTH (Fiber to the Home).
Broader Context and Critical Notes
Directional couplers vary by frequency range (RF, microwave, optical), coupling factor (weak: 20 dB, strong: 3 dB), and medium (coaxial, waveguide, optical fiber). Their design trade-offs—size vs. bandwidth, power handling vs. loss—depend on the application. For instance, 5G networks lean on compact microstrip couplers for base stations, while satellite systems favor waveguide types for durability. The establishment often touts newer designs as universally superior, but older types like branch-line still hold up in niche, cost-sensitive uses—don’t overlook their practicality.
Email us
 High-Current SMD Common Mode Inductor for Power Supply EMI Suppression Low Profile, for Space-Constrained Applications
High-Current SMD Common Mode Inductor for Power Supply EMI Suppression Low Profile, for Space-Constrained Applications High Q SMD Precision Wound Inductor with Low Tolerance for RF Filter Applications
High Q SMD Precision Wound Inductor with Low Tolerance for RF Filter Applications Communication Common Mode Inductor
Communication Common Mode Inductor Ceramic Inductor: High Frequency Ceramic Inductors for RF Applications
Ceramic Inductor: High Frequency Ceramic Inductors for RF Applications Flat Wire Inductor: High Efficiency Flat Wire Inductors for Power Applications
Flat Wire Inductor: High Efficiency Flat Wire Inductors for Power Applications Directional Couplers
Directional Couplers
- Applications and Types of Directional Couplers in Communication Networks

Directional couplers are essential components in communication networks, widely used for their ability to split, combine, or sample signals while maintaining directionality. Below, I’ll outline thei...
- Understanding the Basics of Directional Couplers in RF Systems
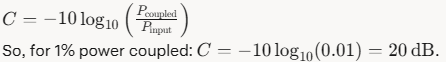
Directional couplers are fundamental components in radio frequency (RF) systems, used to sample a small portion of the signal traveling through a transmission line while maintaining the signal’s dir...
- The Role of Directional Couplers in Microwave and RF Engineering
Directional couplers play a pivotal role in microwave and RF engineering, where their ability to manage high-frequency signals with precision and minimal disruption makes them foundational components....
- Directional Couplers: Key Components for Power Monitoring and Signal Division

Directional couplers are indeed key components for power monitoring and signal division in communication systems. They’re versatile tools that enable precise control and analysis of signals without ...
- Designing Efficient Directional Couplers for Signal Isolation and Coupling

Designing efficient directional couplers for signal isolation and coupling in microwave and RF systems is a balancing act of performance, practicality, and application-specific constraints. These devi...
- Exploring the Performance Characteristics of Directional Couplers in High-Frequency Systems

Exploring the performance characteristics of directional couplers in high-frequency systems (think RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave, from 1 GHz up to 100 GHz or more) reveals why they’re so critic...
- Applications of Power Splitters and Combiners in RF and Microwave Systems

Power splitters and combiners are workhorses in RF and microwave systems, enabling signal distribution and aggregation across a huge range of applications. From splitting a signal to feed multiple ant...
- Understanding Common Mode Chokes: Principles and Applications

Common mode chokes (CMCs) are key players in RF, microwave, and power electronics, designed to tackle common mode noise—unwanted signals that appear simultaneously and in-phase on both lines of a di...
- High Current Power Inductors: Design and Applications

High current power inductors are heavy-duty components built to handle significant current (think 10 A to 100s of A) while storing energy, filtering signals, or managing power in demanding systems. Un...
- Exploring the Performance Characteristics of Directional Couplers in High-Frequency Systems

Exploring the performance characteristics of directional couplers in high-frequency systems (think RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave, from 1 GHz up to 100 GHz or more) reveals why they’re so critic...
- Designing Efficient Directional Couplers for Signal Isolation and Coupling

Designing efficient directional couplers for signal isolation and coupling in microwave and RF systems is a balancing act of performance, practicality, and application-specific constraints. These devi...
- The Role of Directional Couplers in Microwave and RF Engineering

Directional couplers play a pivotal role in microwave and RF engineering, where their ability to manage high-frequency signals with precision and minimal disruption makes them foundational components....
- Directional Couplers: Key Components for Power Monitoring and Signal Division

Directional couplers are indeed key components for power monitoring and signal division in communication systems. They’re versatile tools that enable precise control and analysis of signals without ...
- Applications and Types of Directional Couplers in Communication Networks

Directional couplers are essential components in communication networks, widely used for their ability to split, combine, or sample signals while maintaining directionality. Below, I’ll outline thei...
- Understanding the Basics of Directional Couplers in RF Systems
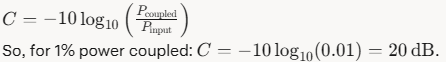
Directional couplers are fundamental components in radio frequency (RF) systems, used to sample a small portion of the signal traveling through a transmission line while maintaining the signal’s dir...
Inductor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000